Unit 13. Biochemistry (FBISE SSC-II Chemistry Keybook)
2. Give short answers.
i. Decide whether sucrose is a disaccharide or monosaccharide. Give reason?
Since Sucrose consists of two monomers, therefore sucrose is a disaccharide. Common names are table sugar, cane sugar or sugar. Sucrose is a disaccharide of glucose and fructose.
ii. What is a dextrose sugar?
Some monosaccharide molecules can rotate the plane of plane polarized light to right (clockwise). They are called dextro-rotatory or dextrose sugars. Glucose, manose, galactose are dextrose sugars.
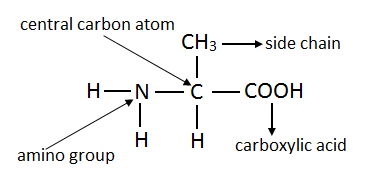
- Write the formula of an amino acid and identify functional groups in it.
An amino acid has two functional groups. All amino acids have a carboxyl and amino group in order for them to form long continuous chains of proteins. Structure of amino acid is as follows: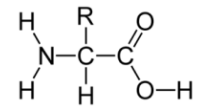
- What is peptide bond?
Molecules of amino acids join together through amino (-NH2) group of one molecule and carboxyl
(-COOH) group of another molecule by eliminating a molecule of water.
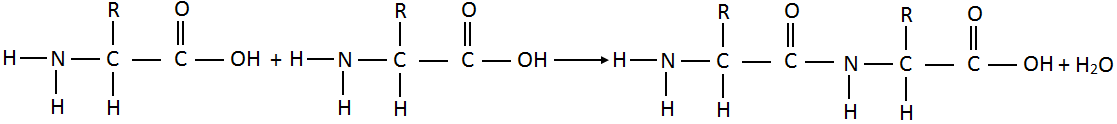
O
||
The linkage – C – NH – which joins two amino acids units is called a peptide bond. The resulting molecule is called dipeptide.
- Which compounds are included in lipids?
- Fats and oils
- Cholesterol
- Reproductive hormones
- Components of cell membrane called phospholipids.
- Some vitamins (A, D, E and K)
- What is the function of DNA?
DNA can store and transmit all the genetic information needed to build organisms. For instance, in human beings the single fertilized egg cell carry the information for making legs, hands, head, liver, heart, kidneys etc. DNA is found primarily in the cell nucleus.
3. Distinguish between mono, di-, and tri-saccharides.
Monosaccharide:
Monosaccharide is simple sugar consists of only one unit. They serve as building blocks for more complex carbohydrate forms. For example Glucose, Fructose, Galactose, Lyxose and Xylose.
Disaccharides:
Disaccharides are group of sugars composed of two monosaccharide groups linked together through the loss of sugar. For example
Maltose = Glucose + Glucose
Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose
Lactose = Glucose + Galactose
Trisaccharides:
Trisaccharides are sugars containing three hexoses. For example Raffinose, found in molasses contain the three hexoses. Nigerotriose, Maltotriose and Melezitose.
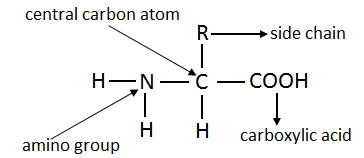
4. Describe bonding in a protein molecule.
Proteins are high molecular weight polymers. The building blocks of all proteins are amino acids. An amino acid has two functional groups. These are carboxylic acid and amino group. Twenty different amino acids are involved in protein synthesis. Out of twenty amino acids, our bodies can synthesize only ten amino acids. Such amino acids are called non-essential amino acids. The remaining ten molecules are called essential amino acids.
Molecules of amino acids join together through amino (-NH2) group of one molecule and carboxyl (-COOH) group of another molecule by eliminating a molecule of water.
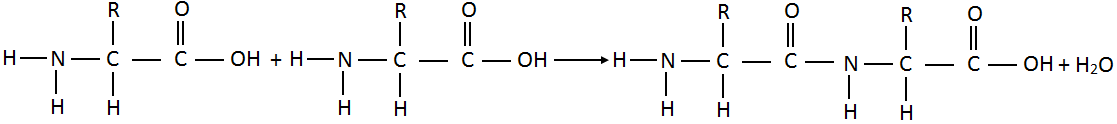
O
||
The linkage – C – NH – which joins two amino acids units is called a peptide bond. The resulting molecule is called dipeptide. There is still an amino group on left and a carboxyl group on right. Each of these groups can further to join more amino acid units. In this way thousands of amino acids units join to form a giant molecule of protein.
5. Explain sources and uses of lipids.
Sources:
- Animals, plants, and marine organisms such as salmon and whales are rich source of lipids.
- Milk is an important source of animal fat from which butter, ghee, ground nut, coconut, olive etc. are good source of vegetable oils.
- Cod liver oil is obtained from salmon and whales.
Uses:
- Butter, ghee and vegetable oils are used for cooking and frying of food, preparing bakery products and sweets.
- In mammals a layer of fat is present under the skin. This layer acts as a thermal insulator.
- Fats protect delicate organs from shocks. A layer of fat around our heart and kidneys protect these organs from injury.
- Lipids provide some vitamins such as A, D and E which are essential for health. These vitamins are insoluble in water and soluble in lipids.
- Fats and oils are important food stores in living organisms. They provide about twice, as much energy per gram as do carbohydrates.
- Vegetable oils are converted into vegetable ghee or margarine by catalytic hydrogenation.
- Fats and oils are also used for the manufacture of materials like soaps and detergents, cosmetic, polishes, paints and varnishes
- In our bodies cholesterol is essential for the synthesis of several hormones, vitamin D and bile acids.
6. Give sources and uses of proteins.
Sources of proteins:
Meat, fish, eggs, milk and cheese are important sources of proteins. Plants also provide us proteins. For example, pulses, beans, meat, egg, fish etc. are rich in proteins.
Uses of Proteins:
- We require proteins in our diet, to provide amino acids to make muscles, hair, enzymes and repair of body tissues.
- Proteins are essential for the formation of protoplasm and components of cells.
- Proteins are essential for both physical and mental growth especially in children.
- A protein called gelatin is obtained by heating bones and tendons in water.
- It is used in bakery goods.
- Enzymes are proteins that catalyse specific biological reactions, without which life would be impossible.
- The antibodies that help us to fight against disease are large protein molecules.
7. Give sources and uses of carbohydrates.
Sources:
- Monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose and galactose are obtained from fruits, vegetables and cerals. They are also present in honey.
- Cellulose is obtained from plants.
- Starch is present in wheat, rice and potato.
- Disacchraide such as sucrose is obtained in sugarcane, sugar beet and fruits.
Uses:
- Carbohydrates store and transport energy in both plants and animals. 1g of glucose provides us 15.6 KJ of energy.
- Starch is used to make rectified spirit by fermentation process.
- Starch is converted to dextrin which is used as an adhesive for stamps and as wallpaper glue.
- Cows, cattle, goats, deer, sheep and termites derive nutrition from cellulose.
- We use cellulose in the form of wood for heat, housing and furniture.
- Wood is also used to make paper and wood pulp.
- Sucrose in used as common table sugar.
8. Differentiate between fats and oils.
|
Fats |
Oils |
|
A lipid is called fat if it is solid at room temperature. |
A lipid is called oil if it is liquid at room temperature. |
|
Mostly derived from animals. |
Mostly derived from plants. |
|
Fats contain larger proportion of saturated fatty acid units. |
Oils contain larger proportion of unsaturated fatty acid units. |
|
Example: Butter fat and beef fat. |
Example: Coconut oil and sunflower oil. |
9. Define and explain vitamins.
Vitamins are specific organic compounds which are required by our bodies to prevent specific diseases but cannot be produced by our bodies. They must be present in our diet in addition to proteins, fats, carbohydrates and minerals. Vitamin D deficiency causes softening of bones. Vitamin B3 deficiency causes inflammation and abnormal pigmentation.
Importance of vitamins:
Vitamins are substances that are essential for our bodies.
Vitamin A:
Vitamin A is important in vision. It helps in the chemical transmission of images from the eye to the brain. It also keeps the cornea moist.
Vitamin C:
Vitamin C is required for the formation of blood and boosting the immune system that protects against illnesses ranging from common cold to cancer.
Vitamin B:
Vitamin B helps to regulate nerve impulse transmissions, in the formation of haemoglobin and activates more than 100 different enzymes.
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D regulates blood calcium. It is necessary for proper bone and tooth growth.
10. Why are vitamins important for us?
Importance of vitamins:
Vitamins are substances that are essential for our bodies.
Vitamin A:
Vitamin A is important in vision. It helps in the chemical transmission of images from the eye to the brain. It also keeps the cornea moist.
Vitamin C:
Vitamin C is required for the formation of blood and boosting the immune system that protects against illnesses ranging from common cold to cancer.
Vitamin B:
Vitamin B helps to regulate nerve impulse transmissions, in the formation of haemoglobin and activates more than 100 different enzymes.
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D regulates blood calcium. It is necessary for proper bone and tooth growth.
11. Describe the importance of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acids are vital components of all life. They are found in every living cell. They serve as the information and control centers of the cell.
12. Explain why agricultural and nutritional sciences are vital.
Protein deficiency leads to physical and mental retardation. Excess lipids or fats may lead to heart diseases or a stroke, cancer, diabetes and other health problems. The nutritional chemists recommend that no more than 30 % of your daily caloric intake come from fat. So, healthy diet is necessary for human growth.
13. Explain hydrogenation of vegetable oil.
Addition of hydrogen to an alkenes is called hydrogenation. This reaction takes place in the presence of Ni, Pd or Pt as catalyst.
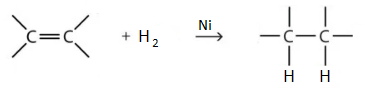
This reaction is used to make margarine or vegetable ghee. Fatty acid component of vegetable oil contains carbon-carbon double bonds. When hydrogen is added to these oils, they become saturated and harder.
14. List commercial uses of enzymes.
Enzymes are large protein molecules. They are biological catalysts. They catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes are also commercially important. They are used in the production of sweeteners, chocolate syrup, bakery products, infant foods, detergents to remove food stains, in cheese making, in paper and pulp industries to remove sticky matter, to prepare fabrics for clothes, furniture and other household items.
15. What is the use of dextrose in drips?
5% m/v aqueous solution of dextrose is used in drips. 5% m/v aqueous solution means 5 grams of dextrose dissolved in water to form 100cm3 of solution. It is intravenously given to patient who is severely dehydrated or is unable to eat or is not allowed to eat.
16. Separate water soluble vitamins from the following. Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Vitamin B.
Water soluble vitamins are: Vitamin A, Vitamin C and Vitamin B.
17. What three elements are important in both proteins and carbohydrates?
Three elements important in both proteins and carbohydrates are Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
18. What is the name of the bond that forms between two amino acids in building a protein?
Peptide bond is formed between two amino acids in building a protein.
19. How many molecules of water are needed to allow a disaccharide to form monosaccharaides?
One molecule of water is needed to allow a disaccharide to form monosaccharaides.
20. Draw the structure of each of the following molecules.
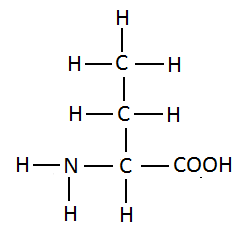
- An amino acid having –CH3 as R group.
- A protein containing two amino acids.
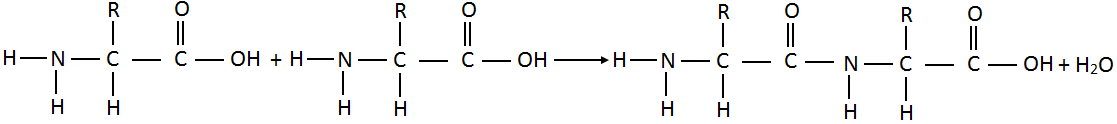
21. What five elements are primarily responsible for the makeup of DNA and RNA?
Elements are primarily responsible for the makeup of DNA and RNA are:
- Carbon
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
22. Write structural formula of an amino acid containing four carbon atoms.
21. Distinguish between DNA and RNA.
|
DNA |
RNA |
|
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. |
RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid. |
|
DNA exists in the form of two strands. |
RNA exists in the form of single strands. |
|
It is made of a deoxyribose sugar, phosphorus unit and nitrogen base. |
It is made of a ribose sugar, phosphorus unit and nitrogen base. |
|
Storing genetic information. |
Transferring genetic information from the DNA to proteins. |
|
For a particular species, the DNA number remains constant for every cell. |
The number of RNA may differ from cell to cell. |
22. Hydrogenation is an important reaction in food industry. Interpret this statement.
The process of hydrogenation involves the addition of hydrogen (H2) to produce a chemical reaction with organic compounds (hydrocarbons). It is hugely important and widely used in the food industry. Hydrogenation is used to convert margarine or vegetable oil into margarine and vegetable ghee in the presence of Ni, Pd or Pt as catalyst.
Self – Assessment Exercise 13.1
1. Classify sucrose, lactose and maltose as mono, di or tri – saccharides. Give reason.
Sucrose:
C12H22O11 + H2O C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
Sucrose Glucose Fructose
So sucrose is di – saccharides of two monosaccharides i.e glucose and fructose.
Lactose:
C12H22O11 + H2O C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
Lactose Glucose Glactose
So Lactose is di – saccharides of two mono saccharides i.e glucose and glactose.
Maltose:
C12H22O11 + H2O C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
Maltose Glucose Glucose
So Maltose is di – saccharides of two mono saccharides i.e glucose and glucose.
2. Is galactose a monosaccharides?
Galactose cannot be hydrolyzed. Galactose is a simple carbohydrate because it consist of only one unit. So galactose is a mono saccharides.
3. Raffinose C18H32O16 hydrolyses as follows. Is raffinose a disaccharides?
C18H32O16 + 2H2O 3C6H12O6
No, raffinose is not a di saccharides. It contain three saccharides so it is a tri – saccharides.
Self – Assessment Exercise 13.2
1. List: a. Three examples of monosaccharides
b. Three examples of disaccharides
c. One example of tri saccharides
d. Two examples of polysaccharides
Monosaccharides: Glucose, Galactose and Fructose.
Disaccharides: Maltose, Lactose and Sucrose.
Tri saccharides: Raffinose.
Polysaccharides: Starch and glycogen.
2. List sources of:
Sucrose: Sucrose is obtained from sugarcane, sugar beet, honey and fruits.
Maltose: Maltose is found in cereals.
Lactose: Lactose is main sugar in dairy product and milk.
Self – Assessment Exercise 13.5
1. How do DNA and RNA differ n structure?
Structure of DNA:
DNA exist in the form of two strands twisted around each other in a spiral formation called double helix. Each chain or strand is made up of a deoxyribose sugar, phosphate unit and a nitrogen base. The strands are held to gather by hydrogen bonds. The order of the base pairs in a strand is a code that stores information which is used to produce proteins.
Structure of RNA:
RNA exist in the form of single strand. It is made of ribose sugar, phosphate unit and nitrogen base. RNA is synthesized by DNA to transmit the genetic information. RNA is responsible for directing synthetic of new proteins.
2. Name two kinds of nucleic acid.
Two nucleic acids are as follows:
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA).
3. Write difference between DNA and RNA.
|
DNA |
RNA |
|
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. |
RNA stands for Ribonucleic acid. |
|
DNA exist in the form of two strands. |
RNA exist in the form of single strand. |
|
DNA is made up of a deoxyribose sugar, phosphate unit and a nitrogen base. |
RNA is made up of a ribose sugar, phosphate unit and nitrogen base. |
|
DNA stores genetic information. |
RNA receives, reads, decode and use genetic information. |
4. What is the sugar unit in DNA?
Deoxyribose sugar unit is present in DNA.
5. What sugar is found in RNA?
Ribose sugar is found in RNA.
6. Which nucleic acid is involved in protein synthesis?
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is involved in protein synthesis.

Recent Comments