Chapter 11 Organic Chemistry (FBISE SSC-II Chemistry Keybook)
2. Give short answers.
i. What is catenation?
The self-linking ability of carbon atoms is called catenation. This ability of carbon results in enormous range of compounds of carbon.
ii. Define isomerism.
Compounds having same molecular formula but different structural formula is called isomers and this process is called isomerism.
iii. Give three examples of alkyle groups.
Examples of alkyle groups:
i. Methyle = CH3 –
ii. Ethyle = CH3CH2 –
iii. Propyle = CH3 – CH2 – CH2 –
iv. Define Functional Group.
An atom or groups of atoms that give a family of organic compounds its characteristics (chemical and physical properties) is called a functional group. For example Carboxyl group, Carbonyl group etc.
- What is difference between an alkane and an alkyle radical?
- Alkane is a hydrocarbon containing only single bonds and have general formula CnH2n+2.
- Alkyle radical is a group of atoms obtained by removing one hydrogen atom from an alkane. Alkyle radicals are represented by symbol R. Their general formula is C nH2n+1.
3. What do you mean by term destructive distillation?
When coal is heated in the absence of air at high temperature, it is converted into coal gas, coal tar and coke. This process is called destructive distillation.
4. List some general properties of organic compounds.
Occurrence:
Most of them come from living things or from the things that were once living.
Covalent nature:
They are generally covalent in nature. They may have polar and non-polar bonds.
Composition:
Carbon is main part of organic compounds. Hydrogen is also frequently present.
Melting and Boiling points:
Generally organic compounds are volatile, so they have low melting and boiling points.
Solubility:
They are non-polar in nature, therefore most of them are soluble in organic solvents like ether, benzene etc. Polar organic compounds are soluble in alcohols such as methyl alcohol.
Homology:
There exist a close relationship between different organic compounds. This similarity in behaviour has made the study of millions of organic compounds easier. They can be classified into few families. A series of related compounds in which any two adjacent molecules differ by -CH2– group is called homologous series.
Reaction rates:
Organic compounds are generally less stable than inorganic compounds. Due to covalent bonding in them, their reaction rates are often slow.
5. List major commercial sources of alkanes.
The major commercial sources of alkanes are coal, natural gas, petroleum and living organism.
Coal:
- Coal is a source of many organic compounds.
- When coal is heated in the absence of air at high temperature, it is converted into coal gas, coal tar and coke. This process is called destructive distillation.
- Coal gas contains methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
- Coal tar is source of many organic compound such as benzene and its derivatives.
Natural Gas:
- Natural gas is a mixture of low boiling hydrocarbons.
- It is mostly methane.
- It also contain ethane, propane and butane.
Petroleum:
- Petroleum contain wide variety of alkanes.
- On fractional distillation petroleum separate into various hydrocarbon components.
Living organisms:
Plants and animals are sources of organic compounds such as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, drugs and medicines.
Synthesis in Laboratory:
More than ten million organic compounds have been prepared in the laboratories.
6. Identify the following compounds on the basis of functional groups they contain.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. What is the name of alkane having seven carbon atoms in the chain?
Heptane (C7H16)
8. What is the name of the alkyl group obtained by removing an end hydrogen atom from:
- Propane:
Propyl
- Ethane:
Ethyl
9. Give the structural formula of two simple alkanes and one alkyne.
Alkanes:

Alkyne:

10. What is meant by term Functional Group?
An atom or groups of atoms that give a family of organic compounds its characteristics (chemical and physical properties) is called a functional group. For example Carboxyl group, Carbonyl group etc.
11. Identify following as an alcohol, aldehyde or ketone.
i. HCHO, which is used to manufacture polymers, such as urotropine which is used to treat urinary tract infection.
Aldehyde because of CHO- group is attached
ii. CH3COCH3, which is used in nail polish remover.
Ketone because of CO- group is attached.
iii. CH3CH2OH, which is used in the preparation of many organic substance such as plastics, cosmetics, tinctures etc.
Alcohol because of OH group is attached to alkyl group.
11. Given a molecular formula of a compound containing C, H and O and single bonds. List all possible functional groups this compound can have?
Functional group containing Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen:
Alcohols:
Alcohols are characterized by the presence of the hydroxyl group(-OH) attached to a carbon chain.
General Formula:
![]()
Example:

Ethers:
Organic compounds that have two alkyl groups attached to the same oxygen atom are called ethers. These compounds have C – O – H linkage in their molecules.
General Formula:
![]()
Example:

12. Give the condensed structural formulas of the following compounds and classify each on the basis of functional group.
|
|
|
|
|
Condensed Structural Formula |
CH3 CH2 CH2OH (1-Propanonol) |
CH3O CH3 (Dimethyl ether) |
|
Functional Group |
Alcohol |
Ether |
13. The diagram represents an organic compound that contains three different elements.

Select the possible compound from the following.
a. Ethanoic acid b. Propene c. Ethanol d. Propane
The compound is Ethanol.
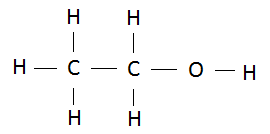
15. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer. It is used for making vinyl sheets, drainage pipes, wire insulation etc. It is obtained from vinyl chloride.

Classify Vinyl chloride as saturated or unsaturated compound.
Vinyl chloride contain double bond between two carbon atoms, so it is unsaturated hydrocarbon.
16. For each of the following, sketch the structural formulas of a two – carbon compound containing the indicated functional group.
|
Alcohol |
|
|
Aldehyde |
|
|
Carboxylic acid |
|
|
Alkene |
|
17. Aspirin is a mild pain killer and fever reducer. It is manufactured from salicylic acid.

Select functional groups present in it and encircle them. Justify your selection.
Functional groups:
- Carboxyl group because two oxygen atoms are attached with a carbon atom.
- Carbonyl group because one oxygen atom is attached with carbon atom.
18. General formula for alkane is CnH2n + 2. Construct the general formula for alkyl radical?
General formula for alkyl radical is CnH2n + 1.
19. Water adds to ethane according to the following reaction.
![]()
Compare the functional groups in the reactant and product molecules.
In reactants:
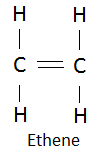
Functional group in the reactant is alkene.
In product:
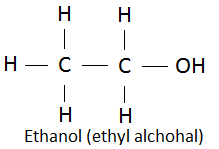
Functional group in the product is alcohol.


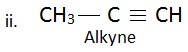









Recent Comments