Unit 14: Atmosphere (FBISE SSC-II Chemistry Keybook)
2. Give short answer
i. List two main sources of acid rain.
Acid rain is caused mainly by the burning of fossil fuels such as coal and gasoline. Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur are released into the air when fossil fuels are burnt and when they mix with the precipitation in clouds acid rain is formed
ii. List four human activities which contribute to air pollution.
- Burning fossil fuel.
- Cutting trees.
- Use of Freon gas.
- Production of methane from dead plant material decay
iii. What is the importance of stratospheric ozone?
Importance of stratospheric ozone:
Ozone saves us from harmful effects of incoming ultraviolet radiations from the sun. When ozone absorbs energy from the sun, the energy’s converted into heat, warming the air. The ozone layer protects the living things on the Earth from dangerous ultraviolet radiation from the sun
iv. What is the role of automobile in air pollution?
Exhaust fumes of automobiles including dangerous gases such as carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen, hydrocarbons and particulates. These exhaust fumes of automobile are responsible for air pollution.
v. Define atmosphere.
Atmosphere:
The envelope of gases and water vapour surrounding the planet earth is called atmosphere
3. Explain temperature variation in stratosphere and troposphere.
Temperature variation in stratosphere:
In the stratosphere temperature varies from -55°C to -5°C.
Temperature variation in troposphere:
As altitude increases in the troposphere, the temperature decreases from 17°C to about -550C. On average for every 1 km increase in altitude, the air gets about 6.5°C cooler
4. List components of stratosphere and troposphere.
Component of stratosphere:
This layer contains little water vapours. Interesting information about this layer is that it contains maximum amount of ozone (about 1Oppm/parts per million). The presence of ozone is responsible for the rise in temperature in stratosphere.
Components of troposphere:
Nearly all the dust particles and water vapours are in the troposphere. Weather occurs in this layer. Most of the clouds are formed in the troposphere. Aircrafts fly in this region.
5. Describe sources of air pollutants.
Sources of Air Pollution:
- Natural Sources:
Many natural processes such as forest fires and dust storms release smoke and dust particles into the air. Volcanoes emit clouds of dust and poisonous gases along with ash. Termites and cows also release large amount of methane in the air. Considerable electrical discharges in the atmosphere produce nitrogen oxides.
- Human Activities:
Most of the air pollution is the result of burning fossil fuels, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas. Nearly half of the air pollution comes from cars and other motor vehicles. Factories and power plants that burn coal or oil release poisonous gases in the air. Burning fossil fuels and incineration release carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NO. NO2) and sulphur oxides (SO2, SO3).
C + 02 (limited) CO
S + 02 SO2
N2 + 02 2NO
2NO + 02 2NO2
Chlorofluorocarbons:
Chlorofluorocarbons have been widely used as solvents for cleaning electronic circuit boards, as refrigerant in fridges and air-conditioning units and as propellants in aerosol sprays (air fresheners, hairsprays, deodorants, spray paints). Such products are not “Environment friendly”. During manufacture, in use and after disposal, these compounds escape into the air.
Lead particles:
Lead particles in the air come mainly due to the combustion of leaded petrol or fuel used in motor vehicles or from lead based paints.
Ozone:
Ozone is produced when electrical discharges pass through oxygen in the air. You can feel its presence near photocopier, television set, microwave oven and other electrical equipment.
Electrical
302 2O3
discharge
6. Describe acid rain and its effects.
Acid Rain:
Acid rain is defined as rain having pH less than 5.6. Normal rain water is saturated with carbon dioxide. It has pH of 5.6 however; the acidity of rain greatly increases in polluted areas during thunderstorm.
Sulphur dioxide from power plants using fossil fuels and nitrogen oxides from exhaust fumes of automobiles dissolve in rain water producing acids.
2S02 + 02 2S03
SO3 + H2O H2SO4
2NO2 + 302 + 2H20 4HNO3
Therefore, during thunderstorm the pH of rain water can be much lower because of sulphuric acid and nitric acids formed by lightening. This rain may have pH as low as 2.1. This value is lower than the pH of vinegar or lemon juice.
Effect of acid rain:
Acid rain may often fall hundreds .of kilometer away from their sources. Acid rain corrodes metals, stone buildings and statues. Marble statues are slowly eroded by acid rain.
Sulphuric acid eats away metals to form water soluble salts and hydrogen.
Fe + H2S04 FeSO4 + H2
Marble buildings and statues:
Marble buildings and statues are disintegrated by acid rain.
CaC03 + H2SO4 CaS04 + H2O + CO2
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 Ca(NO3)2 + H2O + C02
Acid rain also kills fish, and destroys trees. Lakes and river may become too acidic for living things to survive. Trees destroyed by acid rain. Fish are killed by acid rain.
7. Describe ozone depletion and its effects.
Ozone Depletion and Its Effects:
Over recent years, scientists have discovered a reduction in the amount of ozone in the stratosphere.
Ozone hole:
The region in which the amount of ozone has been reduced is called as ozone hole.
Ozone hole was first observed in October, 1980 over Antarctica.
Chlorofluorocarbons:
Chlorofluorocarbons (from aerosol cans, air conditioning systems, refrigerators etc) escape into the atmosphere. CFCs are gases or low boiling liquids. They are so inert that they do not react with any other chemicals in the troposphere. They slowly diffuse into the ozone layer. UV radiation break CFCs molecule producing chlorine free radicals.
CCI3F CCl2F + CI
Chlorine free radical reacts with ozone to form chlorine monoxide (CIO) and molecular oxygen. CIO reacts with atomic oxygen produced by the decomposition of ozone by UV radiations.
.
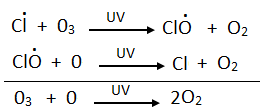
The chlorine free radical that reacts in step 1 is regenerated in step 2. One Cl can destroy thousands of ozone molecules.
8. Describe global warming.
Global warming: The warming of the atmosphere which is due to our influence on the greenhouse effect is known as global warming.
Global warming as a greenhouse effect:
Global warming is due to an upset in the natural balance of the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. If global warming continues, then:
- Temperature of the earth will gradually increase.
- The earth climate may change, affecting both where there is rainfall and how much there is of it. This could cause both increased risks of flooding in some regions and drought in others.
- Polar ice may melt and cause significant increase in sea levels.
- So the atmosphere becomes hotter.
9. Differentiate between stratosphere and troposphere.
|
Troposphere |
Stratosphere |
|
Tropo- means “turning” or “changing”. |
Strato- means “layer” or “spread out”. |
|
It is the first layer of atmosphere. |
It is the second layer of atmosphere. |
|
Height: 0 – 12 km |
Height: 12 – 50 km |
|
Temperature: 170C to -550C |
Temperature: -550C to -50C |
|
It contains dust particles, water vapours and clouds. |
It contains ozone. |
10. Explain ozone formation.
Formation of ozone:
Ozone is an allotropic form of oxygen comprising there oxygen atoms. 03 Ozone is an important gas in the stratosphere.
Most of the ultraviolet (UV) radiations coming from sun are filtered or screened out by the ozone layer Otherwise, sunlight would be much more hazardous for human beings, animals and plants. On absorbing UV radiation, ozone molecule breaks up to form an oxygen molecule and atomic oxygen.
![]()
Atomic oxygen is very reactive. Atomic oxygen reacts readily with an oxygen molecule to form ozone, thereby releasing heat.
![]()
These reactions maintain level of ozone in the stratosphere. Both the destruction and the reformation of ozone are powered by UV radiation. In the absence of outside intervention, the rates of ozone destruction and formation are equal. However, human activities disturb this natural balance.
11. Why is global warming often referred to as the greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect (or accelerated greenhouse effect) is the warming effect caused by all the extra carbon dioxide greenhouse gas that man has put into the atmosphere in the past 100 years by burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas). Global warming is the warming of the earth because of this enhanced greenhouse effect.
12. There is scientific evidence that CFCs contribute to the depletion of ozone. Why?
Ozone hole:
The region in which the amount of ozone has been reduced is called as ozone hole.
Ozone hole was first observed in October, 1980 over Antarctica. The CFCs are so stable that only exposure to strong UV radiation breaks them down. When that happens, the CFC molecule releases atomic chlorine. One chlorine atom can destroy over 100,000 ozone molecules.
13. Sulphur dioxide is a common pollutant from burning coal. State two effects caused by this pollutant.
Sulphur Oxides (SOx):
In the air sulphur dioxide is converted into sulphur trioxide, which is responsible for acid rain. Sulphur dioxide is readily absorbed in the respiratory system. Being powerful irritant, it aggravates the symptoms of people who suffer from asthma, bronchitis, emphysema and other hung diseases.
14. Dibenzothiophene (C12H8S) is a common sulphur containing compound of coal. It is responsible for acid rain. How?
Dibenzothiophene (C12H8S) is a sulphur containing compound of coal on burning it produces sulphur dioxide. In the air sulphur dioxide is converted into sulphur trioxide, which is responsible for acid rain.
15. There have been various attempts to remove sulphur from coal before it is burned. Suggest reason.
Sulphur containing compound of coal on burning produces sulphur dioxide. In the air sulphur dioxide is converted into sulphur trioxide, which is responsible for acid rain. Therefore various attempts to remove sulphur from coal before it is burned have been done.
16. Examine the option there are some ways to reduce pollution caused by cars?
Catalytic converter:
A catalytic converter transforms CO into CO2, NO into N2 and 02, and unburned hydrocarbons to CO2 and H2O. Metals like platinum, palladium and rhodium are used as catalyst in the converter. Government of Pakistan should direct car manufacturers to install catalytic converters in car exhaust system. Government should make strict laws in this regards.
Similar to scrubbers on power plants, catalytic converters reduce NOx emissions from cars.
17. Certain human activities are responsible for a significant increase in green house effect, argue.
Human activities increase the amount of greenhouse gases. These gasses play important role in global warming. Following human activities are responsible for greenhouse effect:
- Cutting forests (deforestation).
- Burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas.
- Household, industrial and livestock waste.
- Use of leaded paints.
18. As a global citizen, how can you play a part to reduce air pollution at a personal level? Argue.
As a global citizen, we take following steps to reduce air pollution at a personal level.
- Walk short distances or ride cycles instead of using vehicles.
- Use Catalytic Converters in vehicles.
- By growing more plants.
- Dispose house hold waste at proper places.
- Use public transport.
19. Compare and contrast between stratosphere and troposphere.
|
Troposphere |
Stratosphere |
|
Tropo- means “turning” or “changing”. |
Strato- means “layer” or “spread out”. |
|
It is the first layer of atmosphere. |
It is the second layer of atmosphere. |
|
Height: 0 – 12 km |
Height: 12 – 50 km |
|
Temperature: 170C to -550C |
Temperature: -550C to -50C |
|
It contains dust particles, water vapours and clouds. |
It contains ozone. |

Recent Comments