Chapter 10 Acids, Bases and Salts (FBISE SSC-II Chemistry Keybook)
2. Give short answers.
i. Write the equation for self-ionization of water?
The reaction in which two water molecules produce ions is called as the self-ionization or auto ionization of water. Simple ionization of water can be written as:
H2O ![]() H+ + OH–
H+ + OH–
A water molecule that loses a proton becomes a negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-). The other water molecule which gains the proton becomes positively charged hydronium ion (H3O+). This can be written as:
2H2O ![]() H3O+ + OH–
H3O+ + OH–
ii. Define and give examples of Arrhenius acids.
Arrhenius Acids:
An acid is a substance that ionizes in water to produce H+ ions. For example:
HCl ![]() H+ + Cl–
H+ + Cl–
H2O
HNO3 ![]() H+ + NO3-1
H+ + NO3-1
Since HCl and HNO3 produce H+ ions, therefore HCl and HNO3 are acids.
iii. Why H+ ion acts as a Lewis acid?
A Lewis acid is a lone pair acceptor, the H+ ion has no electrons, so can easily accept a lone pair from another atom. That is why H+ ion acts as a Lewis acid.
iv. Why NH3 acts as Bronsted-Lowry base?
- According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor.
- Ammonia is a gas at room temperature. When it is dissolved in water, the following reaction takes place.

- Water is proton donor and ammonia is proton accepter. Therefore water acts as an acid and ammonia as a base.
- Why BF3 acts as Lewis acid?

Boron in BF3 has incomplete octet. It has six electrons. So it needs an electron pair to complete its octet. Hence BF3 is an electron pair accepter or Lewis acid.
3. Ammonium hydroxide and nitric acid react and product ammonium nitrate and water. Write balanced chemical equation for this neutralization reaction.
NH4OH + HNO3 NH4NO3 + H2O
4. Write balanced chemical equations for the following neutralization reactions.
a. Sulphuric acid + Magnesium hydroxide Magnesium sulphate + water
H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 MgSO4 + 2H2O
b. Sulphuric acid + Sodium hydroxide Sodium sulphate + water
H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4 + 2H2O
c. Hydrochloric acid + Calcium Hydroxide Calcium Chloride + water
2HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + 2H2O
5. Identify Bronsted-Lowry acids or bases in the following reactions.
a. HNO3 + H2O H3O+ + NO–3
Since HNO3 is converted to NO–3 by donating proton therefore HNO3 is an acid.
Since H2O accepts the proton that HNO3 donates and forms H3O+, water is a base.
b. NH3 + HNO3 NH4NO3
Since HNO3 is converted to NO3– by donating proton therefore HNO3 is an acid.
Since NH3 accepts the proton and forms NH4+ so it is a base.
6. Identify Lewis acid and Lewis base in the following reactions.
a. F– + BF3 [BF4]–
F– has a lone pair on F – atom. So it is electron pair donor. F– is a Lewis base.
Boron in BF3 has incomplete octet. It has six electrons, so it needs an electron pair to complete its octet. Hence BF3 is an electron pair accepter or Lewis acid.
b. H+ + NH3 [NH4]–
A Lewis acid is a lone pair acceptor, the H+ ion has no electrons, so can easily accept a lone pair from another atom. Therefore H + ion acts as a Lewis acid.
NH3 has a lone pair on N-atom. So it is electron pair donor. So, NH3 is a Lewis base.
c. NH3 + AlCl3 [H3N – AlCl3]
In AlCl3, Al is deficient of two electrons. Therefore it will be called Lewis acid.
NH3 contains a lone pair and can be donated to AlCl3 and hence it will act as Lewis base.
7. Classify the following solutions as acidic, basic or neutral.
i. A solution that has hydrogen ion concentration 1.0 x 10-3 M.
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-3 M > 1.0 x 10-7 M
So, solution is acidic.
ii. A solution that has hydrogen ion concentration 1.0 x 10-10 M.
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-10 M < 1.0 x 10-7 M
So, solution is basic.
iii. A solution that has hydroxyl ion concentration 1.0 x 10-3 M.
[H+] = ?
Kw = [H+][OH–]
1.0 x 10-14 = [H+]1.0 x 10-3
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-11 M < 1.0 x 10-7 M
So, solution is basic.
iv. A solution that has hydroxyl ion concentration 1.0 x 10-10 M.
[H+] = ?
Kw = [H+][OH–]
1.0 x 10-14 = [H+]1.0 x 10-10
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-4 M > 1.0 x 10-7 M
So, solution is acid.
8. Classify following substance as Lewis acid and bases. NH3, F – , H2O, BF3
a. Since NH3 accepts the proton and forms NH4+ so it is a base.
b. F– has a lone pair on F-atom. So it is electron pair donor. F– is a Lewis base.
c. Since H2O donate a proton therefore H2O is an acid.
d. Boron in BF3 has incomplete octet. It has six electrons. So it needs an electron pair to complete its octet. Hence BF3 is an electron pair accepter or Lewis acid.
9. Give the Bronsted-Lowry definition of an acid. Write an equation that illustrates the definition.
In 1923 J.N Bronsted and T.M Lowery independently proposed another theory to overcome the shortcomings of Arrhenius theory. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton donor. For example: 
In the above reaction HCl donates proton. So HCl is an acid.
10. Identify Bronsted acids and Bronsted bases in the following.
i. CH3COOH + H2O ![]() CH3COO– + H3O+
CH3COO– + H3O+
- CH3COOH donate proton and become CH3COO–, therefore CH3COOH is an acid.
- H2O accepts proton and become H3O+, therefore H2O is a base.
ii. HCO3– + H2O ![]() CO3-2 + H3O+ (H+ and proton is same)
CO3-2 + H3O+ (H+ and proton is same)
- HCO3– donates proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- H2O accepts proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry base.
iii. NH3 + H2O ![]() NH4+ + OH–
NH4+ + OH–
- H2O donate proton and become OH– , so H2O is an acid.
- NH3 accepts the proton and become NH4+ so it is a base.
iv. HCl + HCO3– ![]() H2CO3 + Cl–
H2CO3 + Cl–
- HCL donates proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- HCO3– accepts proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry base.
v. HS– + H2O ![]() S-2 + H3O+
S-2 + H3O+
- HS– donates proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- H2O accepts proton, so it is the Bronsted –Lowry base.
vi. H2S + NH3 ![]() NH4+ + HS–
NH4+ + HS–
- H2S donate a proton, so H2S is an acid.
- NH3 accepts the proton and become NH4+ so NH3 is a base.
11. Identify the Lewis acids and the Lewis bases in the following reactions.
i. Ag+ + 2CN– Ag(CN2)
- Cation Ag+ is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons.
- Anion CN– is Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons.
ii. B(OH)3 + OH– B(OH)4–
- B(OH)3 is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons.
- Anion OH- is Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons.
iii. Cu+2 + 4NH3 [Cu(NH3)4]+2
- Cation Cu+2 is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons.
- NH3 has a lone pair on N-atom. So it is electron pair donor. NH3 is Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons.
iv. OH– + Al(OH)3 Al(OH)4–
- Al(OH)3 is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons.
- Anion OH– is Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons.
12. Identify Lewis acids and bases from the following.
|
AlCl3 |
AlCl3 is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons. |
|
Ag+ |
Ag+ is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons. |
|
|
Is a Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons. |
|
|
Is a Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons. |
|
CN– |
Anion CN– is Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons. |
|
OH– |
Anion OH– is Lewis base since it is able to donate electrons. |
|
FeCl3 |
FeCl3 is Lewis acid since it is able to accept electrons. |
13. Classify water as proton donor and proton acceptor.
Water is amphoteric in nature. It behave as acid as well as bese. For example,

In this reaction water accepts proton. So water is a base.
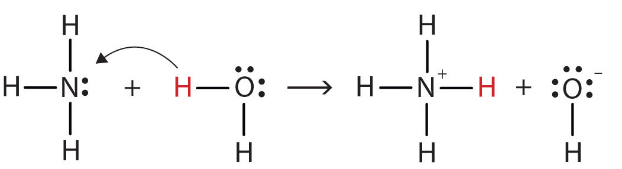
In this reaction water donates proton. So water is an acid.
14. Write equations showing the ionization of following as Arrhenius acids.
a. HI
HI ![]() H+ + I–
H+ + I–
b. HNO2
HNO2 ![]() H+ + NO2-1
H+ + NO2-1
According to Arrhenius theory an acid is a substance that ionizes in water to produce H+. So HI and HNO2 are acids.
15. Write equations showing the ionization of the following as Bronsted-Lowry acids.
a. HNO2
HNO2 + H2O H3O+ + NO–
- HNO2 donate proton and converted to NO– therefore HNO2 is an acid.
- H2O accepts the proton and form H3O+, so water is a base.
b. HCN
HCN + H2O H3O+ + CN–
- HCN donate proton and converted to CN– therefore HCN is an acid.
- H2O accepts the proton and form H3O+, so water is base.
16. Compare the relative concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in each kind of solution?
a. acidic
[OH–] < [H+]
b. basic
[OH–] > [H+]
c. neutral
[OH–] = [H+]
17. Codeine, C18H21NO3 is commonly prescribed as pain killer. It dissolves in water by following reaction.
C18H21NO3 + H2O ![]() [C18H21HNO3]+ + OH–
[C18H21HNO3]+ + OH–
Differentiate Codeine and water as Bronsted-Lowry acid and base.
Codeine is Lewis acid because it is able to accept electrons and water is Lewis base.
18. Examine some ways in which you might determine whether a particular water solution contains an acid or a base.
Three acid-base indicators are:
- Litmus paper
- pH meter
- phenolphthalein indicator
19. The table below shows the colours of two indicators in acidic and alkaline solutions.
|
Indicator |
Colour in acidic solution |
Colour in alkaline solution |
|
A |
Red |
Blue |
|
B |
Colourless |
Red |
- Predict the colour of the indicator A?
- In a solution of pH 3
The solution of pH 3 is acidic, so the colour of indicator A will be red.
- In a solution of pH 10
The solution of pH 10 is alkaline, so the colour of indicator A will be blue.
- Predict the colour of the indicator B in a solution of pH 5?
The solution of pH 5 is acidic, so the colour of indicator B will be blue.
- When a few drops of indicator B are placed in a solution X, it turns red immediately. Evaluate the properties of solution X?
Solution X is alkaline and is basic in nature.
20. Bacteria in our mouth feed on small particles of food stuck to our teeth and change it into acid. Explain how using toothpaste of pH 10 can help to prevent the acid from damaging our teeth?
Toothpaste of pH 10 mildly alkaline. The alkaline pH of toothpaste helps to neutralize the plaque acids which cause tooth decay.
21. Can a substance be a Lewis acid without being a Bronsted – Lowery acid? Argue
Yes, a substance can be a Lewis acid without being a Bronsted – Lowery acid. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton donor. BF3 behave as acid but it does not have ability to donate proton. Nature of such substances cannot be explained by Bronsted-Lowry theory. It can be explained by Lewis theory, which states that:
“A Lewis acid is substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond.”

Boron in BF3 has incomplete octet. It has six electrons. So it needs an electron pair to complete its octet. Hence BF3 is an electron pair accepter or Lewis acid.

Recent Comments